How Web Accessibility and SEO crossover
Updated 2025. Posted 2015 | By Farzana Irani, Web Consultant at iAdControl.com
Disability and accessibility facts:
- Over 1 billion people of the world's population live with some form of disability, according to World Health Organization.
- 16 million people in the UK live with disability, according to Scope.
- A 2019 report indicates that online retailers are losing £17 billion annually by ignoring accessibility needs; this is known as the 'Click-Away Pound.
- The UK's Purple Pound is the combined spending power of disabled people and their households, worth £274 billion annually.
- Global Accessibility Awareness Day occurs on the third Thursday of May.
Web accessibility and SEO improvements help:
- people with disabilities to navigate your website content cohesively
- designing for inclusivity and reaching a wider audience
- meet the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
- search engines to rank your website higher in search results
- to tap into the Click-Away Pound in online retail sales
- to address Corporate Social Responsibility
Website improvements are a formidable wedlock between all types of web users and search engines.
So let's relay the crossover between web accessibility and SEO...
Page title tags
For SEO purposes, page title tags allow search engines to understand the relevancy of your page with the initial part of the title having the most important keywords and phrases. The keywords should be made use of in the most natural and user-friendly manner. The title tag should match the potential visitor's intent. One of the most important on-page ranking factor.
Page title tags display in search engines results and the browser tab area of websites but are hidden on actual web pages.
Page titles should be unique per page as you don’t know what page your visitors will land on. They also should not be the same title as the H1 on the page.
Title tags should ideally be between 50-60 characters with spacing otherwise it will truncate into dots in Google’s search engines. Character limits are subject to change.
We searched for Huffington Post on Google... the title tags sets the tone and relevance of a web page.
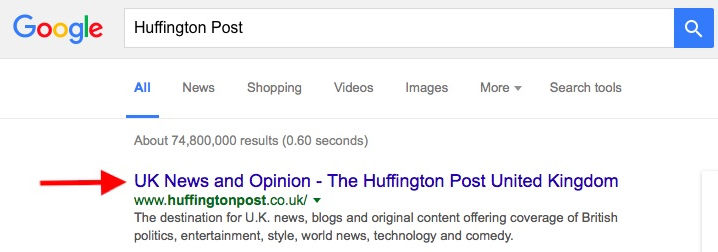

On the actual Huffington Post website, you can view the same title in the browser tab, where the arrow is pointing above.
When using assistive technology such as VoiceOver, NVDA, JAWS (screen readers) for people who may have visual disabilities, the title tag will read aloud whatever is specified. This is why your website should have different titles for each page.
The title tags are one of the first elements to be read out by screen readers.
Please note, this will display if website owners integrate the title and meta tags on their website. If you don’t add specific text you want your web users to see, then Google will generate content from your web page automatically in the title if they deem it suitable. Sometimes Google will also mix it up even if you did add a page title, depending on what the potential visitor searched for.
Also, when you share your website page on social media, the page title will display.
In the HTML code below, the title tag is shown for Huffington Post's homepage. If we added this as text on here, the HTML would have picked up and hidden it as mentioned earlier, therefore, we had to display this as an image.
So it's good practice to make each page title relevant, appealing and click-worthy as possible as they are rich snippet ads of your website.
Headings (H1, H2, H3...)
The use of headings and sub-headings with relevant keywords flowing seamlessly improves your SEO rankings.
Headings should be unique per page. The headings should match the users intent to indicate the relevancy of your page. Use up to 70 Characters. All character limits are subject to change.
Headings also break down chunks of content and enables the user to easily scan your pages, which is great for all types of users. Headings and subheadings structure's the content as the user goes through the page. It's better than having one page full of just text as this immediately puts the user off reading further.
Headings are particularly great for website accessibility too, as people with visual impairment who are using assistive technology can tab through the headings and select which content they wish to be read out. Screen readers can also identify the heading level.
H1 should be used once per page, subsequently, H2, H3, H4, and so on, they can be used more than once depending on the hierarchy of the content.

Image alt tags and alt text
Alt text describes what the image represents. It's short for alternative text.
This is great for people using assistive technology, as it will read what the image is about, if implemented. Alt tags are very useful for the visually impaired so describe images as specifically as possible that’s valuable to the user
Alt tags are first and foremost for accessibility hence it's called alternative text then comes SEO.
For SEO purposes, if you explain the image as well as put relevant keywords as closely related to the image, search engines will count this part of their algorithm and the image will be indexed too.
Use up to 120 characters (including spacing) for alt text - this accommodates the JAWS screen reader alt text field. In some caes longer descriptions can be helpful. Don't include "image of" or "picture of" in the alt text.
Alt tags should be integrated for all your images to describe their meaning, especially if they are functional and informative images. If it’s a decorative image, which is no use to the end user then you should leave the text area null i.e. alt="". When using screen readers it will skip over a null alt text completely, this is what sighted users would do, therefore don't just put keywords in there for SEO gains for these types of images.
This is what the WCAG 1.1.1 guidelines Level A state about Non-text Content:
"Decoration, Formatting, Invisible: If non-text content is pure decoration, is used only for visual formatting, or is not presented to users, then it is implemented in a way that it can be ignored by assistive technology."
This HTML code example includes the image file name, the dimension of the image and the alt tag at the end:

In WordPress, alt tags can be easily updated in the media library.
Also, when the Internet is not working properly sometimes the image won’t load but the alternative text will display instead - same applies when the images are missing, or the image file names are incorrectly implemented.
In some web browsers, when you hover over an image, the alt tag will pop up.
Anchor text / internal links
All links should be meaningful when it comes to SEO and web accessibility.
Link text should be less than 100 characters.
Links in your content, linking to other pages are known as anchor text.
Do not use ‘click here’ or ‘find out more’ to describe a link as it does not assist the disabled user where the link text alone will navigate to - it has to be meaningful on its own. Web visitors navigating via keyboard or screen readers can choose to read out the link text and they can also tab through a list of links. So if the links all stated 'click here', the links would be completely useless to them.
Generic links will not help search engines either to understand the importance of the anchor text. So when linking to another page, specify exactly where the link will go to with 2-3 relevant keywords. Internal linking can also improve link equity throughout other pages on your website.
Do not overuse anchor texts and overstuff with keywords, as it will be counted as spam. If the links are relevant, flows well and has high usability than its fine.
Apparently, only the first anchor text counts in Google if they both are going to the same page.
The anchor text link is underlined in the example shown here of steel garden sheds.

File naming convention
Ensure your web page URLs are SEO-friendly by using the most important and meaningful keywords that are relevant to the page itself.
For web file names, hyphens are the preferred method for separating words due to their readability. Although underscores are recognized by search engines and won't harm your SEO, spaces in between words should always be avoided.
E.g. our marketing services page, we‘ve named it: www.iadcontrol.com/marketing-services
Here’s a bad practice page file name that will hinder Google ranking your pages. The URL alone does not tell web users or search engines what the page is about: page_name_564
People using screen readers can also set their preferences to read image file names.
Sitemaps
For SEO purposes, it is crucial your website has a sitemap.xml as it ensures your website is seen to be as Google-friendly as possible. The sitemap lists all the URLs on your website and allow search engines to crawl your website more intelligently, it also includes additional information such as your websites latest updates and frequency of changes.
If you have quite a large website, then it is always handy to have a dedicated sitemap page to list all the content links of your website in a hierarchical manner. This sitemap makes it easy for visitors to access information effectively and makes every page accessible on one page.
People using assistive technology are likely to use the sitemap page as the main source for navigating through websites quickly to find what they are searching for.
Information Architecture (IA)
Without good user experience, usability and information architecture, no amount of optimisation will help your website’s rankings or aid people with disabilities.
Organising information and implementing content in a structure that's comprehensible, and searchable is critical to SEO.
Breadcrumb trail is another way to show the users where they are located in relation to your website, particularly if your website has deep routed pages. This is sufficient to aid the user in navigating your website and improves the User Experience (UX).
Breadcrumb trails are usually displayed just below the main menu:
iAdControl Blog › The Importance of Information Architecture
On most websites, the current menu tab you are on is highlighted - this is a quick visual aid to indicate the user's main location.
Your main focus should be on the users - providing them with valuable content and your secondary focus should be for search engines.
Make your website built for purpose with high quality content. Structure and position information where the user is most likely to find it.
As stated earlier, when your content is labelled correctly, every element of the page becomes meaningful.
Website code quality
Having the latest, clean and compliant HTML 5 code means that your website can be read by the widest possible range of browsers, devices and are less likely to break your website page. Correct semantic HTML mark up and website code governance helps all types of users and less likely to disrupt screen readers as they go through the sections of pages.
Do not use any styling elements hard-coded within the HTML - have this in the actual CSS file.
Use relevant and meaningful keywords in content, have paragraph spaces, no long sentences, etc.
Complying with W3C Markup Validator is good for keep your code clean.
The above updates will gradually help your website to climb up the search listings and simultaneously enhancing web accessibility.
There is so much more to integrate when it comes to web accessibility but this is a start... so let's get accessible!
Further web accessibility resources
- The SEO and Web Accessibility power couple: Supercharged by AI
- Web Accessibility Initiative
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.2
- How to meet WCAG (quick reference guide)
- Digital accessibility and SEO best practices (TPGi)
- Introducing digital accessibility video
- Making your service accessible
- Cards for humanity - practical tool for inclusive design
- Designing for accessibility
- BBC’s accessibility 'how to guides'
- AbilityNet accessibility resources
- Alt text tips from a person with vision impairment
- International Association of Accessibility Professionals (IAAP)
- CAPTCHA - Human or robot de facto standard defective
- Make the web a better experience
Web accessibility testing tools
- WAVE - Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool
- WebAIM’s Colour Contrast Checker
- Adobe's Colour Contrast Checker
- deque's Axe accessibility testing tool
- The ARC Toolkit by TPGi (Chrome extension)
- An introduction to screen readers
- Microsoft browser DevTools
- JavaScript bookmarklets for accessibility testing
- Web accessibility tools by W3C
- General web tools to optimise your website

